Templates
The initial program 'skeleton' observations were replaced in 2012B with much more complete template observations based on the examples in the OT instrument libraries. This page describes the features related to the use of the template observations.
Template Groups
Template groups for science observations are found in the new "Templates" folder at the top of the program. Inside the Templates folder exists a "Template Group" for each configuration requested in the Phase-I proposal.
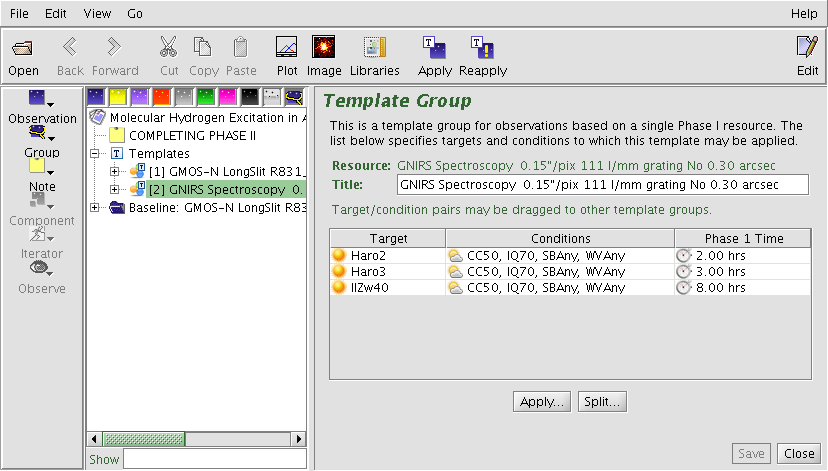
Template observations may be accompanied by baseline calibration observations in separate "Baseline" folders. These typically include observations which will be executed once per instrumental configuraton, e.g. twilight flats, nod & shuffle darks, and spectrophotometric standards.
The targets approved in the Phase I proposal may be viewed by clicking on the "Template Group" nodes which are labeled according to the instrument configuration, e.g. "GMOS-N LongSlit R831...". This list includes the approved observing conditions and the total integration times. Targets may be moved between templates using drag and drop.
Template Regeneration
The libraries and rules used to generate the templates are maintained in a web service. The templates will be updated each semester and as new modes are commisisoned or procedures updated. The templates may be regenerated from the server at any time that you are connected to the internet. The Regenerate button is located in the "Templates" Folder (below) or in the Templates option of the righ-click menu, or via the Menu bar: Edit > Template > Regenerate.
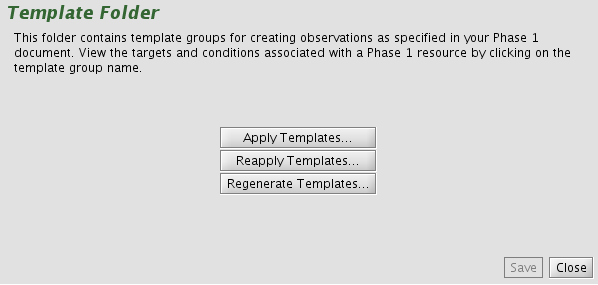
Selecting "Regenerate" brings up the "Template and Calibration Regeneration" window:

If "Add a new copy of the templates" is selected, the current templates will be preserved as well as the links between these templates and any observations created from them. Associated targets may be moved (via drag & drop) to the new tempates when the new templates are created or kept in their current groups.
Any Baseline calibration observations that are added to a separate 'Baseline' folder that are regenerated are always added to a new folder.
Template Splitting
Template Groups may be "split" to create a new group which may be configured independently from the original group. This allows for changes in observing strategy (i.e., acquisitions, offset patterns, etc.) for different targets. To split a Template Group, select the group and click the "Split..." button at the bottom. This will bring up a dialog box to select which targets and conditions should be moved to the new Template Group:

The new Template Group will have a running number appended to the group number (in brackets) to help identify it's origin. This new group may now be modified as needed.
Applying Templates
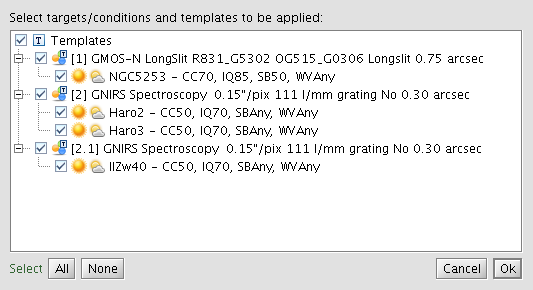
When satisfied with the templates, they may be "applied" to any or all of the associated targets to create real observations. This is accomplished by clicking the "Apply" button on the Main Toolbar or via the right mouse button "Template" menu, or via the Edit > Template drop-down in the Menu Bar. The Apply Template window is shown below and here it is possible to select any or all of the approved targets. The "apply" process creates a copy of the template and adds the target and observing conditions.
Reapplying Templates
After a template has been applied to create observations, it is possible to make bulk changes to those observations by updating the template and then re-applying the template to the relevant observations. This will modify existing observations so that they match the template, keeping only the target node and position angle unchanged.

Phase 2" indicating that the detailed definition of the observation is in progress.
Observations are set to "For Review" to indicate that they are ready for checking by the Principal Support staff who provides Phase II support*. Observations are set to "In Review" to indicate that the Principal Support staff are actively reviewing them. If any problems are found then may be set back to "Phase 2" for further work by the PI.Observations are set to "For Activation" to indicate that they are ready for final verification by the Additional Support staff *. If any problems are found then they may be marked back to "For Review" or "Phase 2" for further work by the Principal Support staff or the PI."On Hold" observations are either active templates for Target of Opportunity triggers or are waiting for an external event, such as the arrival of a MOS mask.Observations marked "Prepared/Ready" may be selected by the observer for execution.* For newly commissioned instruments or modes where Gemini staff provide Phase II support, observations that are correctly defined pass directly from "For Review" to "Ready".
Responsibilities During Phase II Process
During the Phase II cycle illustrated above, the process to be followed and actions to be taken by Principal Investigators, Principal Support staff and Additional Support staff are as follows:
| Gemini | Before the start of the semester, creates skeleton science programs in Observing Database. Emails PI (or Joint Proposal Principal Contact, PC) with the unique key assigned to their program. Emails National Offices with keys for supporting that partners Phase II observations. |
| Investigators (PI / PC) | The PI or PC (or anyone to whom they have delegated responsibility) uses the current Observing Tool to sync the skeleton science program from Observing Database. The Sync option is available from the main toolbar in the science program editor, from the File menu, or with Cmd/Ctrl-s. |
|
The PI or PC uses OT to define details of some or all observations *. During this phase the all edits by the PI/PC are saved automatially to the local database (on their local disk). The program can be exported as an XML file for backup (see the loading/saving maintenance options). *For GMOS MOS programs, pre-imaging observations and complete MOS spectroscopy template groups must be defined by the regular Phase II deadlines. Once the masks have been designed and submitted by the PI there will be opportunities for small revisions to the MOS spectroscopic observations defined by the PI as needed . |
|
|
Once they are satisfied with the observation details, the user sets observation status flag(s) to For Review and then syncs the science program into the Observing Database (using the toolbar button or the File...Sync menu option in the science program editor). The newly-defined observations are merged automatically with the existing contents of the Observing Database (ODB). If the observations have status Phase 2 or For Review in the ODB, then changes made in the local database are copied to the ODB. However, if the observations have status In Review or higher in the ODB then a sync conflict will need to be resolved. Note that PIs can only change the observation status between Phase 2 and For Review. (The reverse change is available so that a PI can change their mind about the status).
|
|
| Setting the status flags and storing the science program causes the Observing Database to notify automatically the relevant National Office and Gemini support staff that one or more observations are awaiting review. | |
| Principal Support | Upon notification that observations are ready for review, the Principal Support contact uses the OT to retrieve relevant science programs from the Observing Database using the same sync option available to PIs and checks observation details. The NGO key or User key allows them to access all programs for which they are responsible for Phase II support. |
| The Principal Support staff member should set all the observations that they are reviewing to status In Review and store the program in order to prevent any changes during the review process. | |
| If an observation checks OK, the Principal Support contact sets observation status flag to For Activation and uses the OT to store the science program into the Observing Database. The PI and the Additional Support staff are automatically notified that one or more observations are awaiting final verification. If the Principal Support is a Gemini staff member, then the observations may be set directly to Prepared. | |
| If observation are found to have problems, the Principal Support staff member sets the observation status flag back to Phase 2 and stores the science program into the Observing Database. The PI is automatically notified that one or more observations need further work. PI and support staff work to resolve the problems off-line, e.g., using the Gemini Helpdesk. | |
| Additional Support | Upon notification that observations are set to For Activation, the Additional Support contact uses the OT to examine relevant science programs from the Observing Database. (Gemini staff have access to all programs.) |
| If an observation checks out, then the observation status flag is set to On Hold or Prepared (equivalent to Ready). If the observation is set to Prepared then the PI and all support staff are automatically notified that it is active in the queue. | |
| If observation details are found to have problems, the observation status flags are set back to For Review and the PI and Principal Support staff are automatically notified that one or more observations need further attention. |
Science Program Tabs
File Attachment tab
Auxiliary files for the program such as Phase I files, mask design files, finding charts, and special ephemerides can be uploaded and download using the File Attachment tab on the top-level science program node. New programs include the files from the Phase I proposal (PIT XML, PDF attachment, and summary PDF).
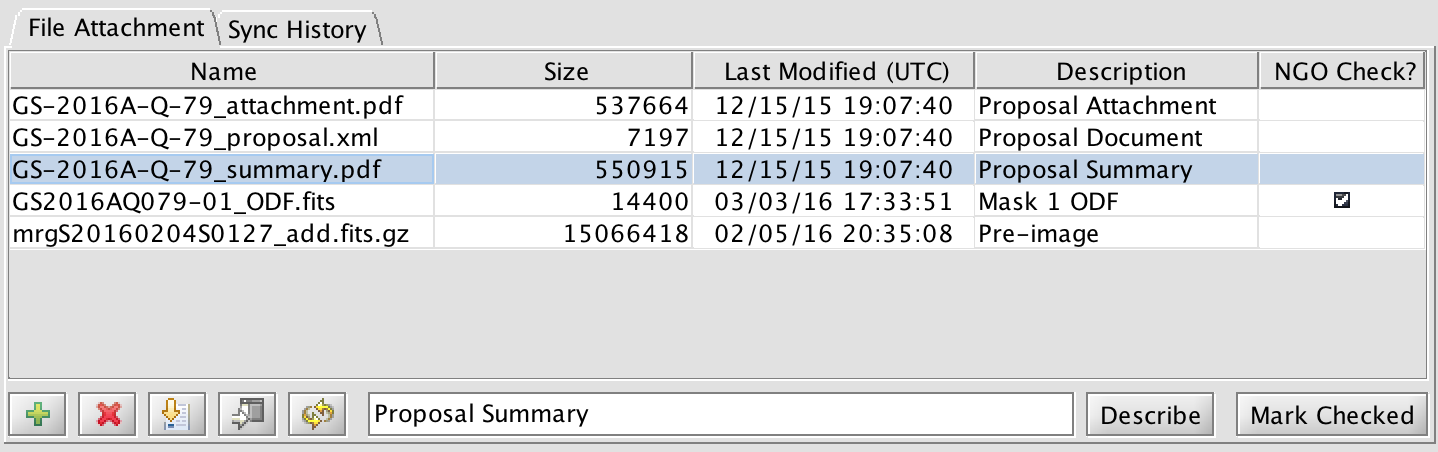
Drag the boundary line between the column titles to change the column width. Selecting a row in the table will activate all of the buttons along the bottom of the tab. The possible actions are:
| Add (upload) a new file. Clicking this will bring up a file selection dialog. Navigate to the proper directory, select the file or enter the file name, and click Attach. | |
| Remove the selected file from the ODB server. | |
| Download the selected file to the local machine. A file dialog will appear. Select or enter the path to the director where the file will be stored. Then click Store. The file will be saved with the same name as given in the table. | |
| Download and display the selected PDF or image file and view it in the default application. | |
| Refresh the attachment table. |
When a line is highlighted you may enter a short description in the text box. Then click the Describe button to save the text.
Program checkers will be able to toggle the "NGO Check" status. This is to inform Gemini that mask designs or finder charts have been checked and are acceptable for continued processing.
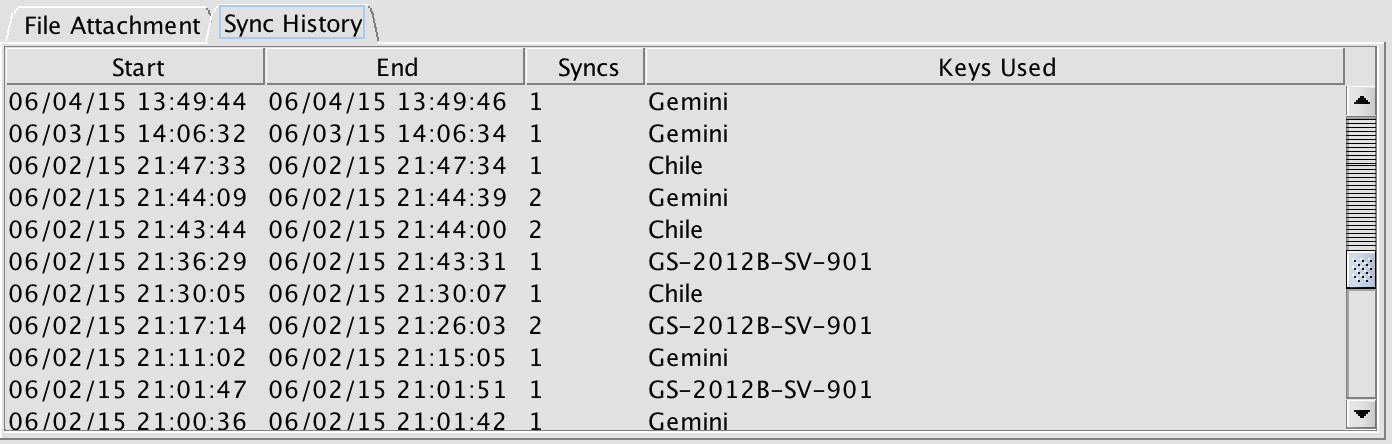
Sync History tab
As the name suggests, the Sync History tab contains time stamps for when the program was synced with the relevant Gemini Observing Database (ODB). The table shows the number of syncs within the given periods of the time and the key that was used. This can help identify who made a given change.