Click on the arrows to navigate through the different steps.
The information below concerns the performance of GeMS in terms of delivered image quality (FWHM) and delivered Strehl. Also provided is information about the NGS Wave Front Sensors limiting magnitudes, sky coverage, PSF uniformity and limitations to observe with GeMS due to the natural seeing and weather conditions, and the elevation of the science targets. The sensitivity, photometric zero points and throughput obtained with GeMS and GSAOI can be found in the GSAOI web page.
How to find the best NGS Asterism
GeMS needs natural guide stars to compensate for Tip-Tilt and Plate Scale modes. They can also be used to compensate for the differential flexure between Canopus and GSAOI and to compensate for the slow variation of the sodium layer altitude.
At the beginning of the GeMS+GSAOI operation, *only one guiding mode* will be available: 3 CANOPUS TTGS (CWFS). Other combinations are being tested and exercised. Complementary information can be found here.
Restrictions due to the LGS
Use of the Laser Guide Star imposes some restrictions
LCH window
Targets must be submitted to the Laser Clearing House at least one week in advance. Usually, each target will have 1 to 5 shutter windows. Typical shutter window are of the amount of few seconds only. Nevertheless, this creates some overheads, as we need to open all the laser and laser related loops, and re-close them once window is cleared. We estimate that the overheads due to LCH window is about 1 to 3 minutes / observation hour.
|
GeMS consist of three main subsystems:
All of these subsystems are linked together by loops and offloads. GeMS can feed two dedicated instruments: GSAOI and Flamingos2.
Gemini South Laser
GS Laser History:
The Gemini South (GS) Observatory acquired a 50W sodium Guide Star Laser System back in March 2010, as one of the key components of the Gemini Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics System (GeMS) project. After a successful post-delivery acceptance in the laboratory, the system was installed on the elevation platform of the telescope.

Beam Transfer Optics
The Laser Guide Star Facility (LGSF) provides the telescope Adaptive Optics (AO) facility with a source of coherent light for the optical excitation of the mesospheric sodium layer to enable the production of an artificial beacon source or “guide star”.

CANOPUS
Canopus is the Adaptive Optics bench of GeMS .
We briefly present the basic AO principles and how anisoplanatism affects the off-axis image quality. The basic principles of MCAO are then presented together with the parameters of the Gemini MCAO.
ALTAIR Component
The detailed component editor for ALTAIR is accessed in the usual manner, by selecting the ALTAIR component in your science program, and is shown here:
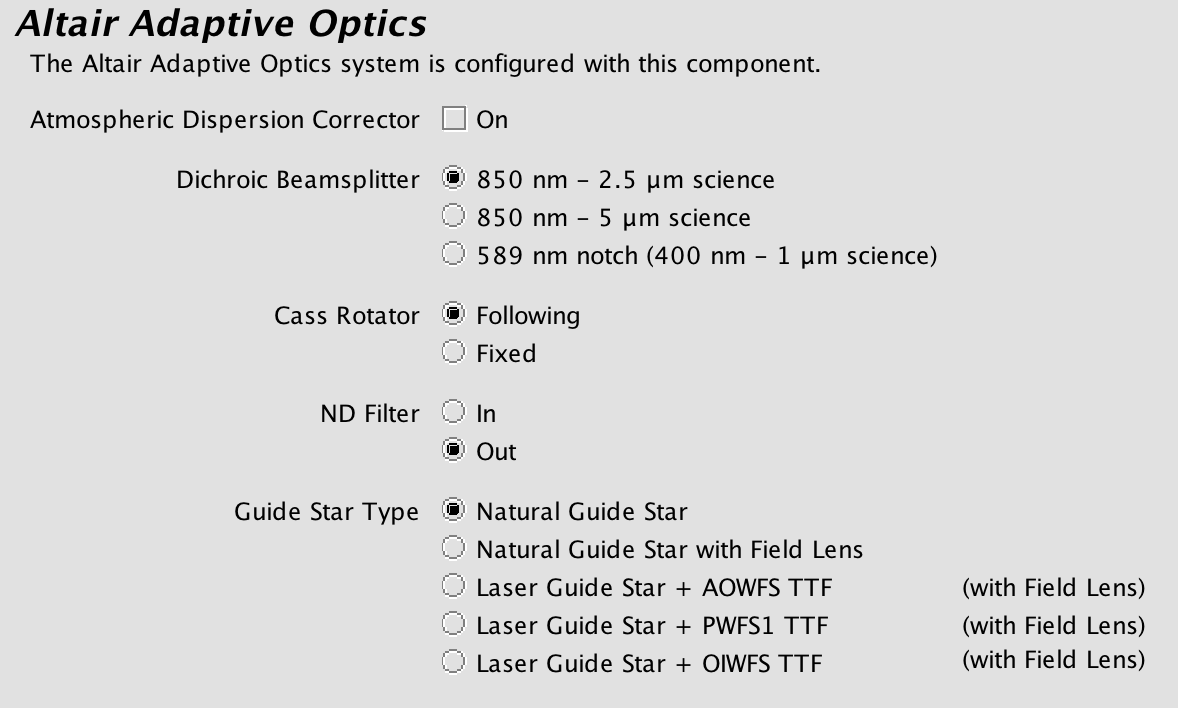
The Atmospheric Dispersion Corrector
Target Component
The specification of the Target component differs somewhat depending on whether a Natural Guide Star (NGS) or the Laser Guide Star (LGS) is being employed. There also can be differences in the target component, depending on whether NIRI or NIFS is being used, since the NIFS OIWFS can be employed to provide tip/tilt information.
Phase II (OT) Checklist
Altair is an Adaptive Optics instrument with no science detector. Here we cover only the checklist important for Altair use, not the specific science instruments which collect the data. Please ensure that you also follow the checklist for your current instrument. Special Instructions for LGS
This page gives a brief introduction to how LGS target lists are generated and used. This is especially important for LGS Standard Target of Opportunity (SToO) programs, but some information is relevant to all Phase II preparations involving LGS.
The ALTAIR field lens is designed to provide better Strehl ratios and sharper image quality at large distances from the guide star, essentially reducing the anisoplanatism of the system.
Sensitivity and Overheads
For sensitivities of ALTAIR use the GNIRS, NIRI, or NIFS Integration Time Calculators. However, please see here for some restrictions regarding use of the ITC, including use at L'. Corrected Image Quality
Introduction
The delivered Strehl ratio (the ratio of the delivered peak intensity to the theoretical peak intensity) is dependent on many factors, such as the natural seeing and stability of the atmosphere, the wavelength of the observations, the brightness of the guide star, the separation between the science target and the guide star, and of course the performance of the telescope and adaptive optics system. Image Library
(Examples of NGS - AO - NIRI Setups)
Natural Guide Star (NGS)
ALTAIR with NGS uses a natural guide star (of sufficient brightness and sufficiently close to the science target, as described below) to monitor distortions in the incident wavefront and correct for them using the deformable mirror as well as provide tip/tilt corrections to the telescope's secondary mirror. Laser Guide Star (LGS)
The Gemini Mauna Kea Laser Guide Star (LGS) System is designed to extend the use of ALTAIR for targets for which a bright natural guide star (NGS) is unavailable for adaptive optics correction. In general, LGS AO delivers somewhat lower Strehls than NGS AO, but it allows the use of fainter natural guide stars (because the guide star is used only for tip/tilt correction) and thus is possible over a much larger fraction of the sky than NGS AO. "Super Seeing" mode (LGS + P1)
Contents
New Instrument Procurement Models
Gemini is implementing a more flexible and enhanced approach to instrument procurement that facilitates development of new instruments and capabilities within the current constraints of our staff and financial resource budgets. In its May, 2014 meeting, the Gemini Board approved new elements of an expanded procurement model, allowing Gemini to work more closely with build teams to support several varieties of in-kind contributions. In the future, we pla Integration and Testing at Gemini
New instruments and systems will undergo several stages of integration and testing (I&T) with the final stage occuring at the telescope itself. Gemini sees value in working closely with instrument teams during both pre-delivery and post-delivery I&T.
Pre-Delivery Expectations for I&T
Gemini advocates for a strong pre-delivery I&T program, for several reasons.
| | | | |


